
Neuroplasticity and Cannabis: How THC May Rewire Learning Pathways
The human brain is not a static organ. It has the remarkable ability to adapt, reorganize, and form new connections
FREE SHIPPING ON ORDERS OVER $99 | 10 points = $1
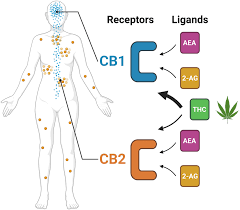
The human body is home to many complex systems that regulate various functions, from digestion to mood and immune response. One lesser-known but incredibly important system is the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Discovered in the 1990s, the ECS plays a vital role in maintaining balance, or homeostasis, throughout the body. Understanding this system helps explain how substances like cannabinoids (found in cannabis and hemp) interact with our body to promote wellness.
Scientists initially discovered the ECS while researching how THC (the main psychoactive compound in cannabis) affects the body. To their surprise, they found that the human body naturally produces its own cannabinoids, called endocannabinoids, which interact with specific receptors. This groundbreaking discovery opened the door to a deeper understanding of how the body maintains balance and responds to internal and external stress.
The ECS is made up of three main parts:
Endocannabinoids are molecules made by the body to help regulate various processes. The two most well-known are:
These compounds are produced on-demand by the body when needed, unlike hormones that are stored for later use.
These receptors are found throughout the body and act as communication hubs for endocannabinoids. The two primary types are:
Endocannabinoids bind to these receptors, triggering signals that help the body maintain balance.
Enzymes in the ECS break down endocannabinoids once they’ve completed their task. The two main enzymes are:
The primary job of the ECS is to maintain homeostasis, meaning balance within the body’s internal environment. Whenever something disrupts this balance—like pain, stress, or injury—the ECS steps in to help bring things back to normal.
The ECS plays a major role in controlling emotional responses. It’s involved in the regulation of mood, stress levels, and even mental health conditions like anxiety and depression.
By interacting with CB1 and CB2 receptors, the ECS helps modulate how the body perceives pain and controls inflammation. This is one reason cannabinoids like CBD (Cannabidiol) are studied for their potential in managing chronic pain.
The ECS also influences hunger signals. Ever heard of the “munchies” after using cannabis? That’s due to the ECS stimulating appetite through CB1 receptors in the brain.
Through CB2 receptors, the ECS helps regulate immune response and inflammation, making it an essential player in defending the body from illness and injury.
Cannabis plants produce compounds called phytocannabinoids, like THC and CBD, which interact with the ECS.
Research into the ECS is still evolving, but understanding its functions helps explain why cannabinoids are being studied for:
Supporting ECS function through lifestyle, diet, and potentially with cannabinoids like CBD may contribute to better overall wellness.
The endocannabinoid system is a powerful internal network responsible for keeping many body systems in harmony. Although still a relatively new field of study, the ECS explains much about how both naturally produced and plant-derived cannabinoids can influence physical and mental health. As research continues, the ECS is proving to be a key player in the pursuit of optimal well-being.

The human brain is not a static organ. It has the remarkable ability to adapt, reorganize, and form new connections

In our fast-paced world, many people accumulate what’s known as sleep debt—a deficit that builds when you consistently sleep fewer